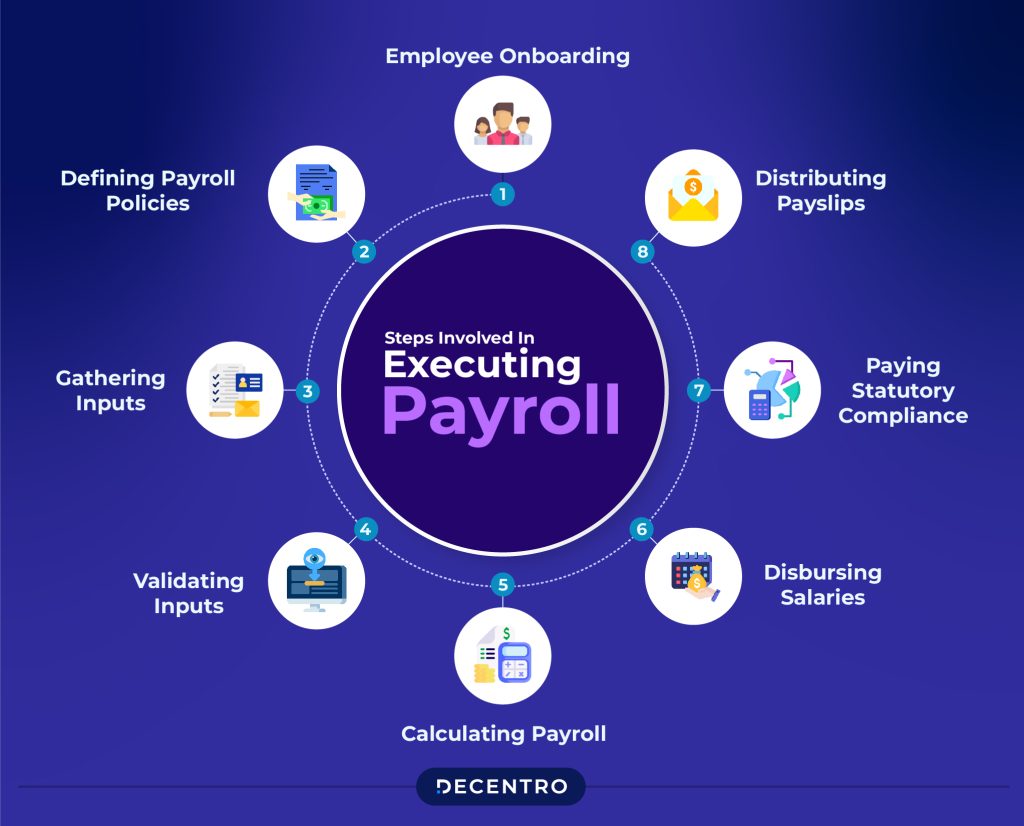
Key Takeaways:
Automating payroll functions can streamline operations, reduce errors, and enhance compliance, saving significant time and cost. However, the decision to adopt payroll automation should be underpinned by careful analysis and preparations. Understanding your current business needs, evaluating available resources, and assessing employee readiness are fundamental steps in ensuring a smooth transition to automated payroll systems. This guide outlines the critical factors businesses should consider before shifting, emphasizing the transformative potential of payroll automation.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Understanding the Benefits of Payroll Automation
- Assessing Your Current Payroll System
- Evaluating Your Business Needs
- Employee Readiness and Training
- Budget Considerations
- Selection of Payroll Automation Vendors
- Ensuring Compliance and Security
- Conclusion
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced business environment, automation is becoming a pivotal part of streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency. One area where automation can have a profound impact is payroll management. Shifting to an automated payroll system can offer numerous benefits, from reducing manual errors to ensuring compliance with ever-changing regulations. However, transitioning to payroll automation requires thorough preparation and consideration of various factors to ensure its success. This article explores key considerations businesses must evaluate to determine their readiness for payroll automation, laying out a roadmap for seamless integration.
Understanding the Benefits of Payroll Automation
Embracing payroll automation brings many advantages that can positively influence a business’s bottom line and employee satisfaction. Adopting payroll software enables organizations to automate repetitive payroll tasks such as calculating wages, withholding taxes, and processing payments efficiently. One of the significant wins of automating these tasks is reducing manual errors, which can be costly and time-consuming. Automated systems ensure compliance with legal and tax obligations through accurate and up-to-date processing, thereby minimizing the risk of penalties associated with non-compliance.
Moreover, payroll automation frees up significant time for the HR department, allowing personnel to focus on more strategic and value-driven activities instead of being bogged down by administrative tasks. The increased efficiency also leads to faster payroll processing, ensuring employees are paid on time, directly contributing to improved employee satisfaction and morale. Furthermore, automation can provide detailed analytics and reporting features, offering insights into workforce management that can be harnessed to make informed business decisions.
Assessing Your Current Payroll System
Before diving into payroll automation, conducting a comprehensive assessment of your current payroll system is crucial. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of your existing setup will help identify the key areas that will benefit most from automation. This evaluation should include analyzing the time spent on payroll tasks, error rates, compliance issues, and overall employee satisfaction with the current payroll process. Such a review will provide a clear picture of the specific needs and pain points that payroll automation can address, ensuring that the transition focuses on enhancing performance and resolving existing issues.
Evaluating Your Business Needs
Every business has unique requirements to consider when deciding to automate payroll processes. Factors such as the size of your workforce, the frequency of payroll runs, and the complexity of payroll calculations should be reviewed. Small businesses may have different requirements than larger corporations with more intricate payroll structures, including bonuses, commissions, and benefits. In this regard, clearly understanding your business payroll needs will guide you in selecting the right payroll automation solution that aligns with your organizational goals and objectives. These insights will also aid in setting realistic expectations for the outcomes of payroll automation.
Employee Readiness and Training
Employees are at the heart of any successful technological transition, making their readiness and acceptance of new systems essential. Payroll automation may bring about significant changes in routine payroll operations, so it is imperative to inform and prepare staff adequately. Engaging employees early in the automation process and seeking their input can foster a positive reception of new systems. Tailored training programs should be designed to equip payroll staff with the necessary skills to operate the new system efficiently.
Additionally, communicating the benefits of automated systems to employees, such as increased accuracy and faster processing times, can help alleviate any concerns or resistance. Comprehensive training allows employees to adapt to using the system effortlessly, ensuring productivity is upheld during and after the transition. This preparation can also ensure that the payroll system integrates seamlessly with existing HR processes, reducing disruptions and promoting consistency across all functions.
Budget Considerations
Implementing payroll automation can involve initial and ongoing costs, which should be carefully evaluated as part of the decision-making process. The budget should account for the cost of acquiring and implementing the new system, including software purchases, setup, and any necessary customizations to meet specific business needs. Additionally, consider the costs of training staff and any potential downtime during the transition phase. While the initial investment may appear considerable, it is crucial to weigh this against the long-term savings and benefits that automation can bring.
These benefits include reduced operational costs, fewer errors leading to financial penalties, and increased efficiency across payroll processes. The projected return on investment (ROI) should be calculated to illustrate the economic benefits of payroll automation over time. Businesses should also undertake a thorough cost-benefit analysis to ensure payroll automation aligns with their financial capabilities and delivers anticipated value.
Selection of Payroll Automation Vendors
Choosing the right vendor for your payroll automation needs is a critical component of the process. You should thoroughly research and evaluate potential vendors based on several factors, including their industry experience, software features and scalability, and customer service reputation. Look for solutions that offer customizable features that can grow alongside your business, providing flexibility to adapt to future changes and expansion.
Examining vendor references and reviews from current users can provide valuable insights into the software’s performance and reliability: prompt customer support and training resources from the vendor can ensure a smoother transition period. Selecting a vendor that offers comprehensive and ongoing support services ensures continuous optimization and update of the payroll system to meet evolving business needs. It is also essential to ensure that the software can integrate effortlessly with existing systems to enhance operational efficiency.
Ensuring Compliance and Security
Payroll data is inherently sensitive, handling critical employee information such as salaries and personal details. Therefore, any payroll automation system’s security and compliance features should be critically examined before selection. The system should have robust data protection measures such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular data backups to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Additionally, compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR, is necessary for any payroll automation system. Regular security audits and updates offered by the vendor can provide peace of mind in maintaining data integrity. Ensuring that the automated payroll system complies with various labor laws and tax requirements across different jurisdictions will help businesses minimize the risk associated with non-compliance, safeguarding against potential legal issues down the line.
Conclusion
Transitioning to payroll automation is a strategic move that can significantly enhance business efficiency and accuracy, leading to substantial time and cost savings. By carefully considering key aspects such as understanding the benefits, assessing current systems, evaluating business needs, ensuring employee readiness, budgeting, vendor selection, and compliance, businesses can seamlessly transition to automated payroll systems. Careful planning and thoughtful execution of the implementation process pave the way for realizing the full potential of payroll automation, empowering organizations to focus on their continued growth and success.